선행학습: 미기상학 관련 용어 정리
대기 경계층 (Atmospheric Boundary Layer)
아래 그림: Vertical cross-section showing the distinct nature of the turbulent boundary layer, filled with chaotic motions of many different scales, and the upper troposphere, characterized by gentle undulations. The color indicates the magnitude of the local variation of the density field, increasing from black to yellow. Simulation performed by J. R. Garcia using 5120_5120_840 grid points. (The plane on the top right corner is included for illustration purposes and it is not part of the simulations.)
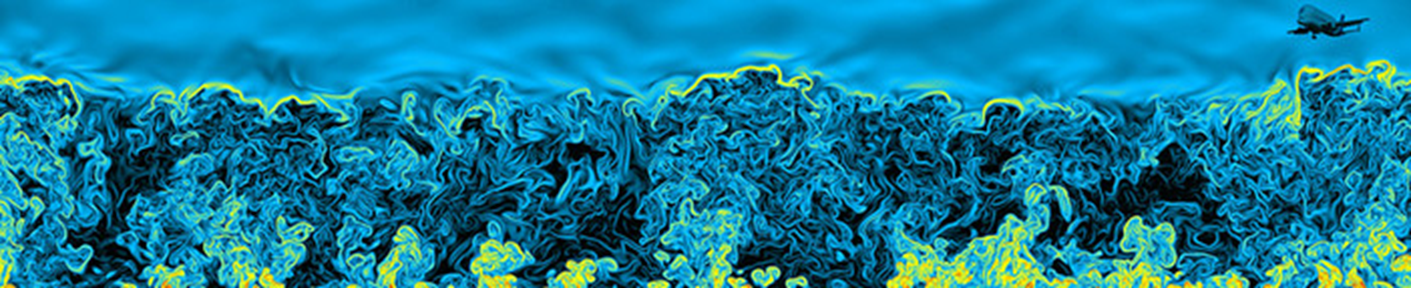
대기 경계층 구조
Planetary boundary layer (PBL) 또는 Atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) 이라 불림.
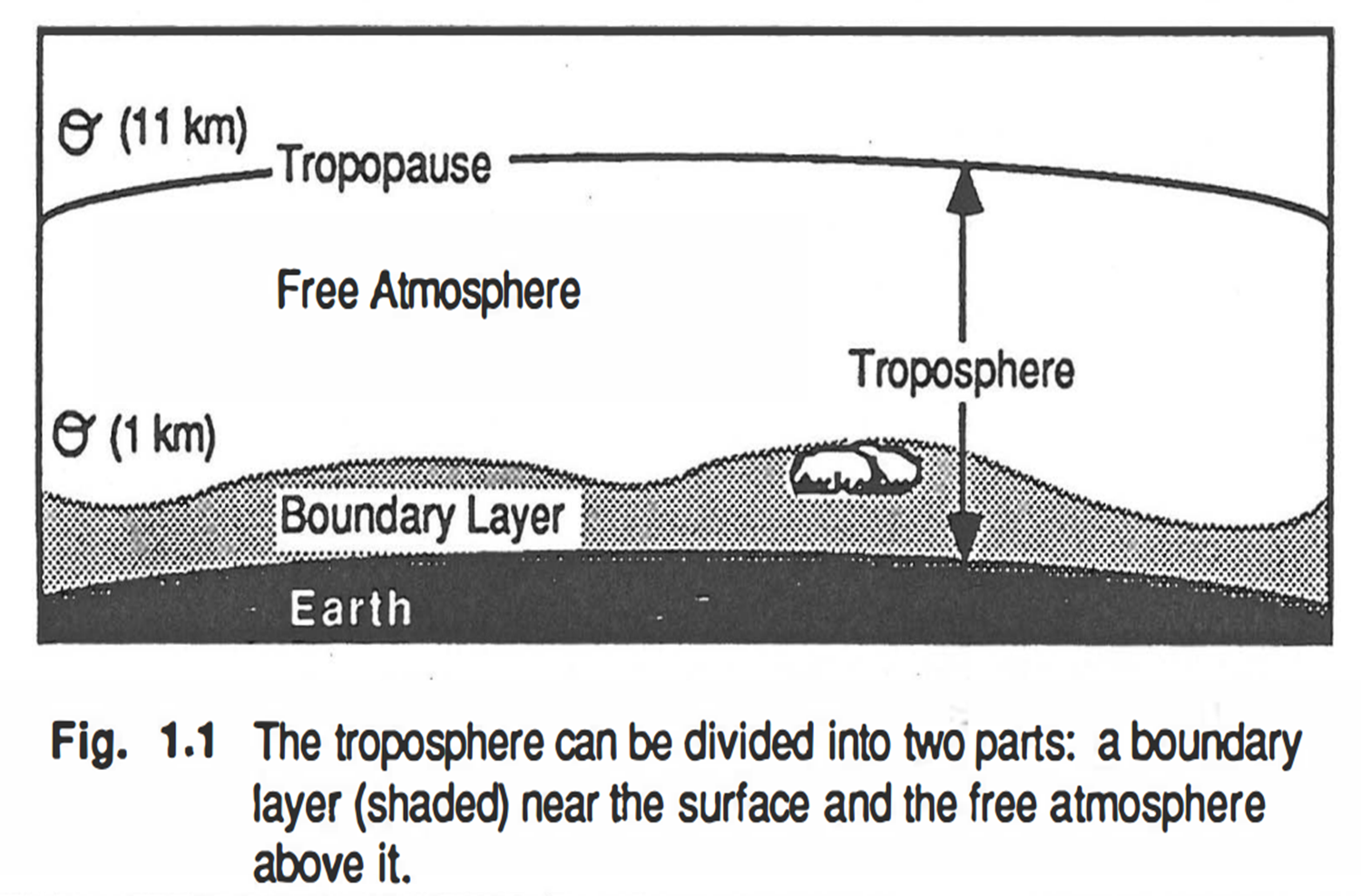

Boundary layer (경계층)
물체 표면과 바로 인접해 이는 유체의 층으로 정의
이 층에서는 momentum, heat, mass의 상당한 교환이 발생 (대기물리에서의 모멘텀)
속도, 온도, 질량 농도가 급격하게 변한다.
Planetary Boundary Layer (대기 경계층)
수 시간~ 약 하루 정도 시간 규모에서 대기-지표 사이의 상호작용의 결과로 형성
지표면 마찰, 가열 등의 영향은 난류 수송(turbulent transfer)나 혼합(mixing)에 의해 즉시 전체 PBL에 전달됨.
PBL = surface layer (지표층) + outer layer (바깥층)

연직 범위:
수십 m ~ 수 km
PBLH (Planetary Boundary Layer Height)
PBLH변동은 중규모와 종관 규모 시스템과 연관있다.

대기 오염의 관점에서 PBL
일반적으로 free atmosphere 보다 훨씬 오염이 심각 (aircraft로 관측)
유체역학 도시 기상학적 관점에서의 PBL

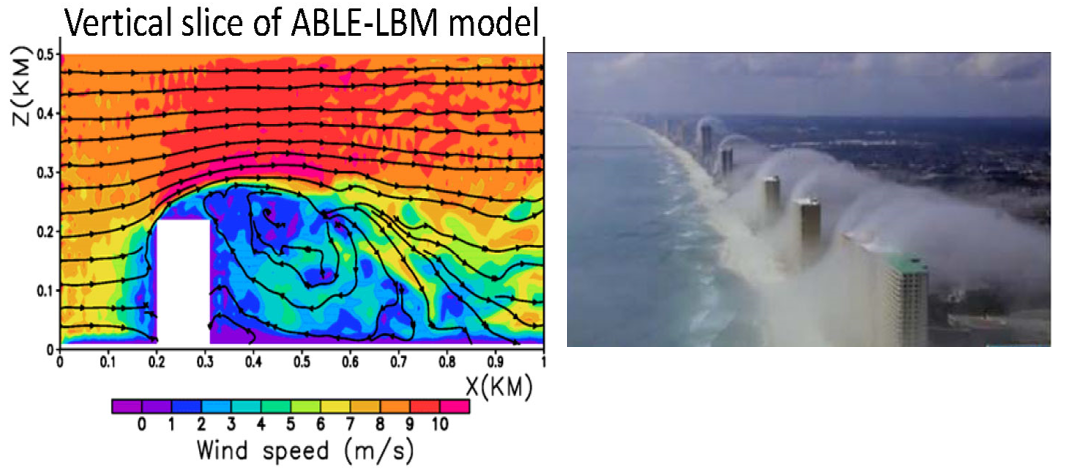
그림 4. Fine-scale turbulent flows over bulings: The ABLE-LBM modeling results (left panel) and the building generated lee-wakes due to colder temperature near building
caused by water vapor condensation.
지표층, 접지층, 거칠기층, 분자아층
미기상학 용어 - 접지층, 지표층, 거칠기층, 분자아층
접지층 또는 지표층(Surface Layer) PBLH의 ~1/10 높이에 이르는 층. 코리올리 효과 무시. 기상 tower에 의해서 관측 가능. 높이에 따른 기상 변수들이 가장 급격하게 변하고, 운동량, 열, 질량 교환도 이
aeir.tistory.com