728x90
반응형
From meteorology to air pollution
Weather <- H2O phase transformation
Air pollution <- gas phase (smog) / particular matter (haze)
Chemical species can be considered H2O in weather

Emissions
natural and anthropogenic inorganic compounds (NOx)
organic compounds(VOC)
Chemical transformation
1. Photochemistry
oxidants: OH, O3
2. Gas−phase and heterogeneous chemistry
"non−volatile" condensed -> aerosols -> dry/wet deposition
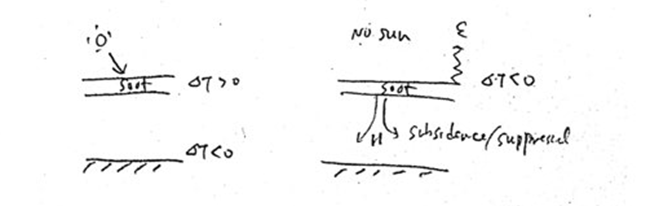
Connection between meteorology and atmospheric chemistry
- Aerosols are the key between two areas
- Cloud formation
- Radiative transformation
- Greenhouse effects (CH4, H2O, CO2, O3, CFCs)
Atmopspheric Chemistry
1. It is related to:
- Organic chemistry (Alkane, Alkenes, Ketones, …)
- Inorganic chemistry (sulfur, nitrogen, halogen compounds)
- Physical chemistry (reaction rate, photolysis)
- Nano chemistry (aerosols)
- Biochemistry (humans, animals, plants)
- Analytical chemistry (measurements)
- Theoretical chemistry (Quantum chemistry)
2. Atmospheric radiation (scattering, absorption, cloud formation, circulations).
3. Observations from fields, lab, and satellites.
4. Numerical simulation
5. Tropospheric chemistry
- Urban
- remote continental
- marine chemistry
6. Stratospheric chemistry
Chemical Processes in the atmosphere

General Oxidation Processes

728x90
반응형